vchal
By Lynn Song
Trade recovery remains modest
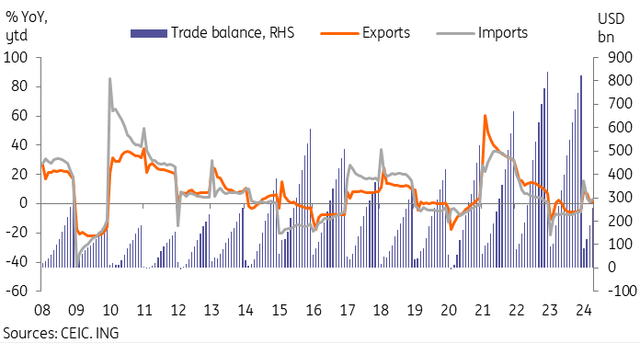
After March’s weak data, April’s trade data recovered slightly. Exports increased by 1.5% year-on-year, while imports increased by 8.4% year-on-year, leading to a trade balance of $72.35 billion.
The April data kept year-to-date (YoY) export growth unchanged at 1.5% year-on-year, while imports increased at 3.2% year-on-year. The trade balance for the first four months of the year stood at $255.7 billion, lower than the $266.0 billion in the same period last year. In RMB terms, which is more relevant for assessing GDP growth, the trade balance stood at RMB 1,817.3 billion since the beginning of the year, slightly lower than the level of 1,829 .0 billion RMB over the comparable period of 2023.
Export and import growth returned to positive levels in April
Key business themes continued to manifest over the past month
By export destination, ASEAN has continued to gain importance for China. Export growth to the region in April was 20.4% year-on-year, bringing the year-to-date growth level to 6.3% year-on-year. In the first four months of the year, ASEAN remained China’s top export destination, accounting for 16.9 percent of total exports. As expected, exports to the United States remained weak, down -1.6% year-on-year in April, for a decline of 1.0% year-to-date. Exports to the EU have also struggled, down 3.3% year-on-year in April and -4.8% year-to-date. It remains to be seen whether President Xi’s trip to Europe, where the focus has been on improving trade relations, will contribute to a recovery in trade in the coming months.
By export product, the performance of different categories remained uneven. Automotive continued to experience strong growth amid China’s strong competitiveness in the NEV sector, up 21.2% year-on-year. The impact of price competition in the automotive sector is also visible in export data; volume growth was even higher, at 26.0% year-on-year. Exports of household appliances were also a surprising area of strength, up 12.6% year-on-year. With domestic demand for home appliances likely to recover after the implementation of recovery policies, the sector may witness a recovery this year. In contrast, steel exports fell sharply by -13.4% year-on-year, and mobile phone exports also fell by -8.5% year-on-year. PMI data showed that export orders increased for two consecutive months, which is a favorable sign, but we expect global external demand conditions will likely be relatively tepid at best this year.
For imports, strength was heavily concentrated in a few categories. The main theme in our opinion is the goal of participating in the AI race. Imports of automatic data processing equipment increased by 49.9% year-on-year, imports of integrated circuits increased by 11.9% year-on-year, and high-tech product category increased by 11.5% year-on-year. % over one year. Many other categories of imported products have seen their growth remain in sharp contraction since the start of the year. Agricultural imports fell by -8.7% year-on-year, coal imports fell by -11.0% year-on-year and cosmetics imports fell by -15.4% year-on-year.
These themes, particularly on the import side, should continue to manifest themselves in the months to come. Given that import demand may remain resilient, but exports will face a higher level of risk in the coming months, we expect trade to contribute less to growth from the second quarter onwards.
Content Disclaimer
This publication has been prepared by ING for information purposes only, regardless of the user’s means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information does not constitute an investment recommendation, nor does it constitute investment, legal or tax advice, or an offer or solicitation to buy or sell any financial instrument. Learn more